Short Summary (TL;DR):
A VPN helps keep you safe and private online by hiding your real location and protecting your data. It prevents websites, hackers, and internet providers from easily tracking your activity, and it can also help you access content blocked in your country. VPNs run quietly in the background and are easy to use, even for beginners.
Have you ever wondered what a Virtual Private Network (VPN) is or how it works? In today’s digital age, understanding VPNs is essential for anyone concerned about online privacy, security, or accessing restricted content. In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about VPNs with clear explanations and practical examples.
What is a VPN?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, creates a secure connection over the internet by encrypting your data and routing it through a server in a different location. This protects your privacy and allows you to browse the web anonymously.
Imagine a VPN as a digital tunnel that safeguards your internet traffic. When you connect to a VPN server, your data is encrypted before it leaves your device. Instead of directly accessing websites, your traffic goes through the VPN server, masking your true IP address. The VPN server then decrypts your traffic and forwards it to the destination website. This entire process ensures that your online activities remain private and secure from prying eyes.
In simpler terms, a VPN allows you to:
- Encrypt your data: Protect sensitive information from hackers or snoopers.
- Hide your IP address: Shield your identity and browsing activities.
- Bypass restrictions: Access content blocked by geographic or institutional controls.
How Does a VPN Work?
A VPN works by establishing an encrypted “tunnel” between your device and a remote VPN server. All your internet traffic passes through this tunnel, ensuring it cannot be intercepted or viewed by others.
Here’s how it works step by step:
- Connect to a VPN: When you connect to a VPN server, your internet traffic is encrypted before it leaves your device.
- Traffic is routed through the VPN server: Instead of directly accessing websites, your traffic goes through the VPN server first, masking your IP address.
- Secure data transfer: The VPN server decrypts your traffic and forwards it to the destination (e.g., a website). The response is encrypted again before reaching you. Therefore, anyone in between (e.g., ISP) cannot track or see your activities.
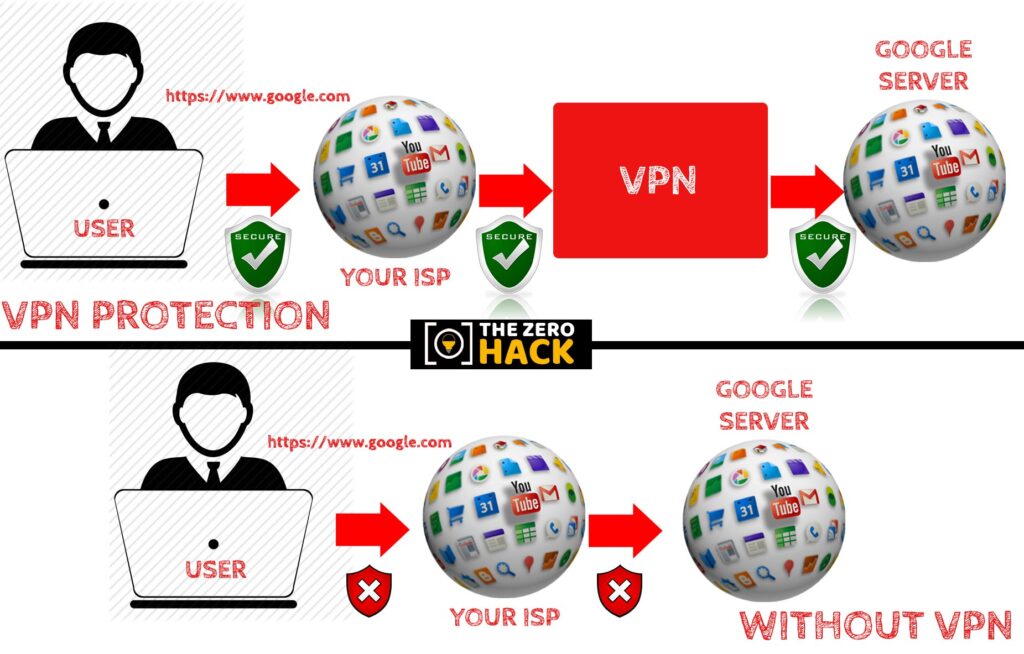
Illustration:
When you visit a website like Google without a VPN, your request directly passes through your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to Google’s server. However, with a VPN, your request is first encrypted and routed through the VPN server. This makes it impossible for anyone, including your ISP, to track your activities.

SSL vs. VPN: Clearing the Confusion
Many people confuse SSL and VPNs, assuming they offer the same level of protection. However, they serve different purposes.
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is the standard technology for establishing an encrypted link between a web server and a browser. This ensures that all data passed between the two remains private and secure. You can identify a website using SSL by the padlock icon and “https://” in the address bar.
- VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) encrypt your entire internet connection and route it through a server in a different location, masking your IP address and providing anonymity.
Here’s the key difference:
- SSL encrypts the data transmitted between your browser and a specific website, preventing others from intercepting the content of your communication.
- VPNs encrypt all your internet traffic and route it through a secure tunnel, hiding your browsing activity from your ISP and anyone else who might be monitoring your connection.
Why Your ISP Can Still See Your Browsing History (Even with SSL)
While SSL encrypts the content of your communication with a website, it doesn’t hide the fact that you’re communicating with that website. Your ISP can still see:
- The websites you visit: Even though they can’t see the specific content, they know you’re accessing a particular site.
- The time and duration of your visits: They have a record of when you accessed a website and for how long.
- Your IP address: This identifies your location and can be linked to your online activity.
How a VPN Enhances Your Privacy
A VPN adds an extra layer of privacy by masking your IP address and encrypting all your traffic, making it much harder for your ISP or anyone else to track your online activity.
In essence:
- SSL protects the content of your communication.
- VPNs protect your entire internet connection and browsing activity.
Why You Need a VPN in Today’s World
While many websites now use HTTPS for secure communication, a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is still crucial for a truly safe and unrestricted online experience. Here’s why:
Security Beyond HTTPS:
- Protecting All Your Traffic: Not every website uses HTTPS. A VPN encrypts all your internet traffic, securing your data even on unencrypted sites and protecting information transmitted by apps that may not use HTTPS.
- Securing Public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi is a hotbed for hackers. Even with HTTPS, vulnerabilities can exist. A VPN encrypts your entire connection, preventing data theft on these networks.
- Preventing ISP Tracking: Your ISP can see everything you do online. A VPN blocks your ISP from monitoring your activity and selling your data.
Expanding Your Online Freedom:
- Bypassing Geo-Restrictions: Many websites and services are blocked in certain countries or regions. A VPN allows you to bypass these restrictions by connecting to a server in another location, granting you access to the content you want. This includes accessing streaming services like Netflix and Hulu, which offer different content libraries depending on your location.
- Accessing Blocked Websites: VPNs can bypass restrictions imposed by workplaces, schools, or governments. If your access to social media or other websites is blocked, a VPN can help you regain access. For more details on accessing blocked websites, check out our article on how to unblock websites.
Enhancing Your Privacy:
- True Online Anonymity: A VPN masks your IP address, making it difficult to track your online activity and location. This is essential for journalists, activists, or anyone concerned about online privacy.
- Protection from Hackers: On public Wi-Fi, hackers can easily intercept your data. A VPN encrypts your information, making it unreadable to hackers.
Additional Benefits:
- Remote Work Access: Many companies use VPNs to allow employees secure access to company resources while working remotely.
- Circumventing Censorship: Some countries heavily censor internet access. A VPN can help you bypass these restrictions and access blocked content.
Real-World Examples of VPN Use
- Secure Online Transactions: When you’re banking online or shopping, a VPN encrypts your connection, protecting your sensitive financial information (like credit card numbers and passwords) from potential hackers. This is especially important when using public Wi-Fi, which is often unsecured.
- Bypass Geo-Restrictions: Streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, and BBC iPlayer have different content libraries in different countries. A VPN allows you to connect to a server in another country and access content that might be blocked in your region. This also applies to other websites and services that may be restricted based on your location.
- Travel with Privacy and Security: When you’re traveling abroad, using a VPN helps you maintain your privacy and security on unfamiliar networks. You can access your usual online services, like banking and email, without worrying about your data being intercepted. Plus, you can use a VPN to bypass censorship in countries with restricted internet access.
- Avoid Price Discrimination: Some airlines and e-commerce websites use your location to show you different prices. By connecting to a VPN server in a different location, you can sometimes find better deals on flights, hotels, and other goods and services.
- Protect Yourself on Public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi hotspots are convenient, but they’re also a prime target for hackers. Using a VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it much harder for anyone to steal your data while you’re connected to public Wi-Fi.
- Improve Your Gaming Experience: A VPN can help reduce lag and latency in online games by connecting you to a server closer to the game server. It can also protect you from DDoS attacks, which can disrupt your gameplay.
- Access Work or School Networks Remotely: Many companies and schools use VPNs to allow employees and students to securely access their networks from home or other remote locations. This allows you to access files, applications, and other resources as if you were on-site.
How to Use a VPN?
Using a VPN is simple. You’ll need to subscribe to a reliable VPN service provider. We’ve curated a list of best free and paid VPN providers to help you choose. Once you’ve chosen a provider, you’ll need to install their VPN app. Most providers have apps for various devices like computers, smartphones, and tablets.
Here’s how to connect:
- Open the VPN app and log in with your account details.
- Choose a server location. This could be a country or a specific city.
- Click the “Connect” button. The app will establish a secure connection.
That’s it! You’re now using a VPN.
Other Ways to Connect
Besides using a VPN app, there are a couple of other ways to connect:
- Inbuilt VPN setup: Some operating systems (like Windows and Linux) have built-in tools for setting up a VPN connection. You’ll usually need server information from your VPN provider to do this.
- Open-source clients: Tech-savvy users can opt for open-source VPN clients like OpenVPN.
Key Features to Look for in a VPN
When choosing a VPN, consider the following: –
- Encryption: Look for 256-bit encryption for maximum security.
- No-logs policy: Ensure the provider does not store your activity logs.
- Speed: A high-speed VPN is essential for streaming or gaming.
- Server locations: More servers in various locations offer better access to global content.
- Compatibility: Check if it works with your device (Windows, macOS, Android, iOS etc.).
Potential Drawbacks of VPNs
While VPNs offer significant benefits for online privacy and security, it’s important to be aware of their limitations:
- Reduced Speeds: Encrypting your data and routing it through an external server can sometimes slow down your internet connection. The extent of this slowdown depends on factors like the VPN provider, the server location, and your own internet speed. Choosing a VPN provider with a large network of servers and optimized protocols can help mitigate this issue.
- Reliability and Trust: It’s crucial to choose a trustworthy VPN provider. Some providers may engage in data logging or other practices that compromise your privacy, even if they claim a “no-logs policy.” Do your research, read reviews, and opt for reputable providers with a proven track record.
- Compatibility Issues: While most VPNs offer user-friendly apps for various devices, you might occasionally encounter compatibility issues with certain websites, apps, or operating systems. This can sometimes require troubleshooting or contacting customer support.
- Cost: While some free VPNs exist, they often come with limitations like data caps, fewer server locations, or even privacy concerns. Reputable VPN services typically require a paid subscription.
- Not a Silver Bullet: VPNs are powerful tools, but they don’t offer complete anonymity or protection. They primarily focus on encrypting your internet traffic and masking your IP address. They don’t protect against things like malware, phishing attacks, or vulnerabilities in the websites you visit.
- Potential for Blocking: Some websites and online services actively try to block VPN users. This is common with streaming platforms trying to enforce geographic restrictions.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: While VPNs are legal in most countries, some governments have restrictions or outright bans on their use. It’s important to be aware of the laws in your country and any countries you may be traveling to.
Conclusion
In today’s digital world, where online privacy and security are increasingly important, VPNs have become indispensable tools. Whether you’re concerned about hackers on public Wi-Fi, want to access geo-blocked content, or simply want to browse the internet with greater peace of mind, a VPN offers a powerful and user-friendly solution.
However, remember that a VPN is just one piece of the puzzle. Staying safe online requires a combination of good practices, including using strong passwords, being cautious about phishing scams, and keeping your software updated.
Do you have any questions about VPNs? Share your thoughts or concerns in the comments below! We’re here to help you navigate the world of online privacy and security.

Please tell me how can i hack my wife facebook account because he always change i know his password.